Togakure Ryū Ninpō – article translation
From Wanderings in Budo by bujinshugyo
戸隠流忍法
木曽義仲の家臣だった戸隠大助が、12世紀の始め頃、戦いに敗れて伊賀に身を隠し、叔父の霞隠道士から骨指術や剣術を始めとする様々な武術を学んで開いた。最初は戸隠流八法秘剣と呼ばれ、時代によって名称は様々に変化した。伊賀忍者の百地三太夫などが学び、紀州藩の取名家を経は、17世紀頃から戸田家に伝わった。戸隠流は、手甲、施盤投げ、手裏剣、水遁の術に使う四尺のしの竹などに特長がある。戸隠流忍法体術は、骨指術からの分家である。
Togakure Ryū Ninpō
Togakure Daisuke was a vassal of Kiso Yoshinaka in the early 12th century, he hid in Iga after losing a battle, from his uncle Kagakure Dōshi he was taught a variety of martial arts beginning with kosshijutsu and kenjutsu. Though the name was changed depending on the period it was first referred to as Togakure ryū happō biken. In the 17th century the Toda family took over the school. Iga ninja such as Momochi Sandayū learnt from the distinguished family when it moved to Kishū province. Specialities of the Togakure ryū are shuko, senban throwing, shuriken and water evasion techniques including the use of a 4 shaku bamboo tube. Togakure ryū ninpō taijutsu is a branch of kosshijutsu.
霞隠 Kagakure – mist hiding, hiding in the mist – also read as Kain.
雲隠 Kumogakure – cloud hiding, hiding in the clouds
道士 Dōshi – a moral person or Taoist
Kagakure and Kumogakure are used interchangeably, both can be seen as coming form the from the homeland of Togakure ryū – the mist sheathed mountain slopes of Iga – as well as the use of smoke to escape that is synonymous with the legend of the Ninja. So you can see Kagakure Dōshi as a religious person who is able to hide in the mists and clouds – this also brings to mind the 修験道 Shugendō idea of being able to subsist through eating mist.
百地三太夫 Momochi Sandayū – a famous ninja who’s exploits appears in many stories.
手甲 Shuko – hand spikes. But also be read as Tekko – hand armour or armoured sleeves.
施盤投げ Senban nage – rotating plate throwing. Although the first character used in the text is 施 which refers to begging or alms so reads ‘begging bowl throwing’ bringing to mind the idea of disguise as a beggar in espionage. The characters for rotating plate are 旋盤.
手裏剣 Shuriken – blade inside the hand, small throwing blade
四尺のしの竹 Yonshaku no Shinodake – 4 length or measure bamboo tube. A shaku is 30.3 cm so the breathing tube is around 1.2 meters.
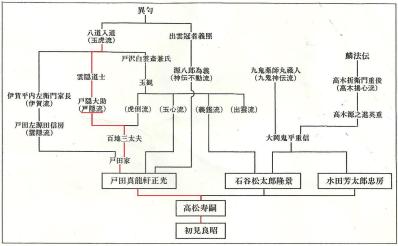
The genealogy chart shows Togakure ryū as coming from the Gyokko ryū of Hachidō Nyūdō through Kagakure Dōshi to Togakure Daisuke. It then passes on though Momochi Sandayū to the Toda family, to Toda Shinryūken Masamitsu, Takamatsu Toshitsugu then Hatsumi Masaaki.